Take a look at our newest merchandise
An intensive HACCP plan is important to maintain management of meals security in a restaurant.
HACCP (Hazard Evaluation and Vital Management Level) is a meals security administration system through which hazards are recognized and managed at particular factors within the meals course of. In a restaurant, a HACCP plan paperwork how you’ll maintain meals protected from organic (e.g., micro organism), chemical (e.g., cleansing chemical substances), and bodily (e.g., glass, steel) hazards at each stage of dealing with and repair.
The USDA and FDA outline the seven HACCP rules as: hazard evaluation, figuring out Vital Management Factors (CCPs), setting essential limits, monitoring, corrective actions, verification, and recordkeeping. An efficient HACCP plan builds on good prerequisite applications (e.g., sanitation, employees coaching, provider management) and applies these seven rules to your particular menu and processes
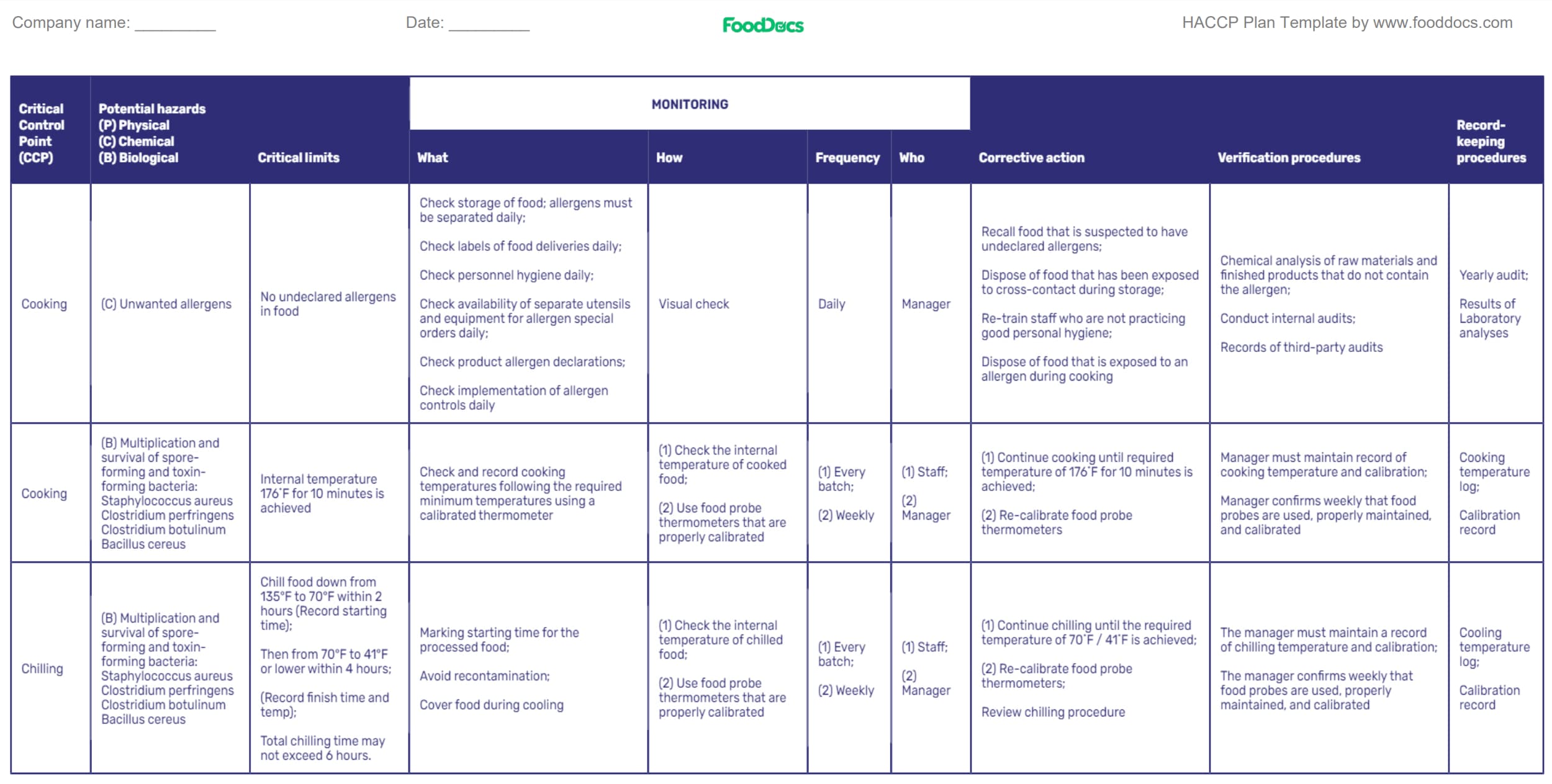
| Vital Management Level (CCP) | Potential hazards (P) Bodily (C) Chemical (B) Organic |
Vital limits | MONITORING | Corrective motion | Verification procedures | File-keeping procedures | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| What | How | Frequency | Who | |||||||
| Cooking | (C) Undesirable allergens | No undeclared allergens in meals | Verify storage of meals; allergens should be separated each day;
Verify labels of meals deliveries each day; Verify personnel hygiene each day; Verify availability of separate utensils and gear for allergen particular orders each day; Verify product allergen declarations; Verify implementation of allergen controls each day |
Visible examine | Each day | Supervisor | Recall meals that’s suspected to have undeclared allergens;
Eliminate meals that has been uncovered to cross-contact throughout storage; Re-train employees who aren’t practising good private hygiene; Eliminate meals that’s uncovered to an allergen throughout cooking |
Chemical evaluation of uncooked supplies and completed merchandise that don’t include the allergen;
Conduct inside audits; Data of third-party audits |
Yearly audit;
Outcomes of Laboratory analyses |
|
| Cooking | (B) Multiplication and survival of spore-forming and toxin-forming micro organism: Staphylococcus aureus Clostridium perfringens Clostridium botulinum Bacillus cereus | Inside temperature 176˚F for 10 minutes is achieved | Verify and document cooking temperatures following the required minimal temperatures utilizing a calibrated thermometer | (1) Verify the interior temperature of cooked meals;
(2) Use meals probe thermometers which are correctly calibrated |
(1) Each batch;
(2) Weekly |
(1) Workers;
(2) Supervisor |
(1) Proceed cooking till required temperature of 176˚F for 10 minutes is achieved;
(2) Re-calibrate meals probe thermometers |
Supervisor should preserve document of cooking temperature and calibration;
Supervisor confirms weekly that meals probes are used, correctly maintained, and calibrated |
Cooking temperature log;
Calibration document |
|
| Chilling | (B) Multiplication and survival of spore-forming and toxin-forming micro organism: Staphylococcus aureus Clostridium perfringens Clostridium botulinum Bacillus cereus | Chill meals down from 135°F to 70°F inside 2 hours (File beginning time);
Then from 70°F to 41°F or decrease inside 4 hours; (File end time and temp); Whole chilling time could not exceed 6 hours. |
Marking beginning time for the processed meals;
Keep away from recontamination; Cowl meals throughout cooling |
(1) Verify the interior temperature of chilled meals;
(2) Use meals probe thermometers which are correctly calibrated |
(1) Each batch;
(2) Weekly |
(1) Workers;
(2) Supervisor |
(1) Proceed chilling till the required temperature of 70˚F / 41˚F is achieved;
(2) Re-calibrate meals probe thermometers; Evaluation chilling process |
The supervisor should preserve a document of chilling temperature and calibration;
The supervisor confirms weekly that meals probes are used, correctly maintained, and calibrated |
Cooling temperature log;
Calibration document |
|
Verify our free instrument
Why are restaurant HACCP plans necessary?
Eating places want HACCP plans to forestall foodborne sickness. CDC information present about 800 foodborne outbreaks are reported yearly within the U.S., and most contain eating places. A written or digital HACCP plan helps cooks and managers proactively management dangers (e.g., cold and hot temperatures, cross-contamination, allergens) as a substitute of reacting after diseases happen.
In addition they align with FDA’s Meals Code philosophy of Energetic Managerial Management, which refers to how administration units insurance policies and checks (slightly than hoping for good luck) to maintain kitchens protected. Word that for many eating places, HACCP is voluntary, however it is strongly recommended. Some specialised processes (e.g., curing, smoking, utilizing components as a substitute of warmth) could legally require a HACCP plan or well being division variance.
In any case, utilizing a HACCP plan demonstrates dedication to meals security and compliance with FDA/USDA tips.
Find out how to write a HACCP plan for a restaurant (step-by-step)
To create a HACCP plan to your restaurant, comply with these steps aligned with FDA/USDA steerage and the seven HACCP rules. Every step ought to be documented. Use bullet lists or tables for readability, and maintain procedures easy to coach employees.
1. Type a HACCP workforce and set up prerequisite applications
Collect a small workforce of key employees (head chef, kitchen supervisor, high quality/security individual) to develop the plan. Evaluation and doc your prerequisite applications (e.g., sanitation SOPs, gear calibration, pest management, worker hygiene, provider approval).
These applications create the inspiration for HACCP. Guarantee all PRPs are up-to-date and auditable. FDA steerage emphasizes that all prerequisite applications ought to be documented and commonly audited as a part of HACCP design.
2. Describe menu gadgets and draw a course of move diagram
Listing the particular meals/processes lined by the plan (e.g., grilled hen sandwich, broiled salmon). Write a short product description (e.g, substances, packaging, shelf life).
Draft a HACCP move diagram that outlines every step of the method from receiving substances to serving. For instance: receiving uncooked hen → storage → thawing/prep → cooking → scorching maintain/serve → cooling leftovers → chilly storage → reheating). Confirm the move on-site. This visible map will information your hazard evaluation.

3. Establish and analyze hazards (HACCP Precept 1)
For every step within the move, checklist potential meals security hazards:
- Organic hazards: Pathogens like Salmonella, Listeria, E. coli that might develop or survive.
- Chemical hazards: Cleansing brokers, allergens, or poisonous meals residues.
- Bodily hazards: Glass, steel shards, bones, or different international objects.
Take into account how every hazard can enter or develop within the meals. For instance, uncooked poultry could carry Salmonella (organic) and bone fragments (bodily). Doc the doubtless hazard(s) at every step.

Take a look at our free hazard evaluation template.
4. Decide Vital Management Factors (HACCP Precept 2)
A CCP is a degree the place you may apply a management measure to forestall or remove a hazard. Use a call logic (e.g., USDA’s CCP choice tree) to resolve if a step is a CCP. Widespread essential management level examples in a restaurant embody cooking and reheating, the place a time/temperature kill-step prevents meals poisoning pathogens.
For instance, cooking hen totally is a CCP as a result of it eliminates Salmonella. Because the FSIS defines: “A Vital Management Level (CCP) is a step in a meals manufacturing course of at which a management will be utilized to forestall, remove, or scale back a meals security hazard to acceptable ranges.” Mark every step in your move as CCP or not, with justification.

5. Set up essential limits for every CCP (HACCP Precept 3)
For each CCP, outline a measurable essential restrict that distinguishes protected from unsafe. These limits are based mostly on science or regulation. For instance, write the essential restrict subsequent to every CCP (e.g., Cooking: Temp ≥165 °F). Non-CCP steps could have “limits” which are preventive (e.g., fridge ≤41 °F as a requirement in Good Practices).
- Cooking: Poultry should attain ≥165 °F (73.9 °C) inside temperature to kill dangerous micro organism. (This FDA/USDA minimal is your essential restrict.)
- Sizzling holding: If cooked hen is held earlier than service, maintain it at ≥135 °F to forestall bacterial progress.
- Cooling: If you happen to cool giant parts, FDA guidelines say cool from 135 °F to 70 °F inside 2 hours, and to 41 °F inside an extra 4 hours. You possibly can mix these as “cool from 135 °F to 41 °F in ≤6 hours”.
- Reheating: Leftover hen ought to be reheated to 165 °F earlier than serving.
6. Arrange monitoring procedures (HACCP Precept 4)
Decide how you’ll examine every CCP (and key limits at non-CCP steps) throughout operation. Monitoring will be steady or periodic (e.g., measuring temperature each batch, or hourly logging of fridge temps). Specify who does it, how, and the way usually.
This might sound one thing like: use a calibrated probe thermometer to examine the interior temperature of every cooked hen batch, or document cooler temperatures twice a shift. CPP monitoring should be documented in logs. (FDA tips say information are wanted to confirm HACCP is working.)
7. Outline corrective actions (HACCP Precept 5)
Use a corrective motion plan to find out what to do if monitoring exhibits a restrict has been exceeded. The motion should guarantee unsafe product isn’t served. Listed here are a few examples:
- If cooked hen measures beneath 165 °F, proceed cooking till the correct temperature is reached after which discard the batch of any product not introduced as much as restrict.
- If fridge temp rises above 41 °F, regulate or restore unit; if meals has been in peril zone too lengthy, discard it.
Write corrective steps for every CCP and every other essential step.

8. Confirm HACCP system (HACCP Precept 6)
Verification means checking that the plan works. This may increasingly embody calibrating thermometers commonly, reviewing information, conducting inside audits, and even microbial testing of completed merchandise. Assign somebody (e.g., QA supervisor) to evaluate HACCP information weekly and confirm that monitoring and corrections had been completed correctly.
Doc these verification actions and periodically validate that essential limits (like cooking temps) are scientifically ample to regulate hazards.
9. Hold documentation and information (HACCP Precept 7)
Preserve all HACCP paperwork together with the plan itself, hazard analyses, and all monitoring logs. Recordkeeping is crucial for compliance and traceability, so maintain calibration certificates, temperature logs, corrective motion varieties, and employees coaching information.
The FDA stresses that an HACCP plan should embody “record-keeping and documentation” procedures. Retailer these information for an outlined interval (e.g., 1-2 years) in case of inspections or audits.

Every of those steps ought to be clearly written in your HACCP plan. Hold explanations concise and action-oriented (e.g., “Management measure: Cook dinner to 165 °F. Monitoring: Use thermometer on every batch”) in order that employees can simply comply with them.
Find out how to preserve and replace your HACCP plan
As soon as your HACCP plan is written, it’s not a set-it-and-forget-it doc. It must be reviewed and up to date commonly to remain related and compliant. Neglecting steady enchancment in your restaurant operations can ultimately result in meals security non-compliance.
That is why eating places ought to:
- Evaluation your complete plan no less than as soon as per yr
- Replace it anytime there’s a main menu change, new gear, or a shift in meals preparation processes
- Reassess hazards and CCPs if introducing a brand new cooking methodology (e.g., sous-vide, smoking, fermentation)
- Doc all revisions with a model quantity and date
- Re-train employees anytime the plan modifications

Well being inspectors or auditors could ask to your most up-to-date model and coaching information, so conserving this present exhibits sturdy managerial management.
Pattern HACCP plan desk: cooking and storing hen
Under is a breakdown of what is included within the restaurant HACCP desk for a typical restaurant course of: cooking uncooked meat corresponding to hen and storing the cooked product. This illustrates the way to checklist steps, hazards, management measures, CCPs, limits, monitoring, and actions.
Nice, right here is the reformatted pattern HACCP plan part out of your article, now offered in a clear, structured bulleted checklist format for higher weblog compatibility:

Receiving Uncooked Rooster
- Hazards: Organic (Salmonella), Bodily (bones), Chemical (residues)
- Preventive Controls: Buy from accepted distributors, examine supply temperature
- CCP: No
- Vital Restrict: Should be ≤ 41 °F at supply
- Monitoring: Log temperature on the time of receipt
- Corrective Motion: Reject shipments above 41 °F
- Verification: Conduct provider audits and spot checks
- Data: Supply temperature logs, provider documentation
Storing Uncooked Rooster
- Hazards: Bacterial progress, cross-contamination
- Preventive Controls: Refrigerate at or beneath 41 °F, retailer uncooked individually
- CCP: No
- Vital Restrict: Fridge temperature ≤ 41 °F
- Monitoring: Log fridge temperatures no less than twice per day
- Corrective Motion: Alter temperature or discard unsafe meals
- Verification: Evaluation logs, examine refrigeration models
- Data: Each day refrigeration logs
Cooking Rooster
- Hazards: Pathogenic micro organism (e.g. Salmonella)
- Preventive Controls: Cook dinner to required inside temperature
- CCP: Sure
- Vital Restrict: Inside temperature ≥ 165 °F
- Monitoring: Verify and document temp of every batch utilizing a calibrated probe thermometer
- Corrective Motion: Proceed cooking till correct temperature is reached
- Verification: Supervisors oversee cooking and calibrate thermometers commonly
- Data: Cooking temperature logs
Sizzling Holding cooked hen (if used)
- Hazards: Bacterial progress if meals cools beneath protected temperature
- Preventive Controls: Preserve meals temperature at or above 135 °F
- CCP: No
- Vital Restrict: Holding temperature ≥ 135 °F
- Monitoring: Carry out hourly temperature checks
- Corrective Motion: Reheat meals to 165 °F or discard
- Verification: Examine and calibrate scorching holding gear
- Data: Sizzling holding temperature logs
Cooling Cooked Rooster
- Hazards: Clostridium perfringens spore progress
- Preventive Controls: Cool meals quickly utilizing shallow pans or ice baths
- CCP: Sure
- Vital Restrict: Cool from 135 °F to 70 °F inside 2 hours, and from 70 °F to 41 °F inside the subsequent 4 hours
- Monitoring: Log temperatures at 2-hour and 6-hour marks
- Corrective Motion: Use speedy cooling strategies; discard if time/temp not met
- Verification: Supervisor critiques cooling logs; examine gear efficiency
- Data: Cooling time and temperature logs
Storing Cooked Rooster
- Hazards: Bacterial progress, cross-contamination
- Preventive Controls: Retailer cooked meals promptly in clear, labeled containers
- CCP: No
- Vital Restrict: Storage temperature ≤ 41 °F
- Monitoring: Verify and log fridge temps each day
- Corrective Motion: Alter fridge or discard meals if in peril zone
- Verification: Gear inspections and periodic log audits
- Data: Storage logs and leftover labels
You possibly can adapt it to your menu and processes. A downloadable PDF model of this pattern template is on the market.
Every row above is annotated as follows:
- Potential meals security hazards checklist the organic (B), chemical (C) or bodily (P) hazards for that step.
- Preventive controls describe the usual protected practices or prerequisite applications in place (e.g., accepted suppliers, sanitation).
- CCP? signifies whether or not that step is designated a Vital Management Level. On this instance, Cooking and Cooling are proven as CCPs as a result of they immediately remove or restrict the expansion of pathogens.
- Vital limits state the security threshold at a CCP (or key restrict for management). For example, cooking hen to an inside temperature of ≥165 °F meets USDA/FDA protected cooking tips.
- Monitoring explains how employees will measure the management. For cooking, it’s “measure inside temp every batch with a thermometer.”
- Corrective Actions element what to do if monitoring exhibits the restrict wasn’t met (e.g., “if temp <165 °F, proceed cooking and re-check”).
- Verification covers audits and checks that the HACCP plan is adopted appropriately (e.g., calibrating units, supervisor critiques).
- Data notes what varieties or logs should be stored (e.g., cooking temp logs, cooling charts).
This pattern plan emphasizes sensible, measurable controls slightly than simply concept. Every essential step has particular standards and actions, guaranteeing compliance with FDA/USDA tips and making coaching easier for employees.
What are the most typical HACCP errors in eating places (and the way to keep away from them)?
Avoiding widespread pitfalls can save your workforce from security dangers and failed inspections. These are the errors seen most frequently in restaurant HACCP plans:
Skipping hazard evaluation
This ends in a obscure or incomplete plan that does not mirror actual meals security dangers. With out clearly figuring out hazards, your controls could miss key dangers like allergen cross-contact or undercooked proteins.
Sensible tip: Use a hazard evaluation worksheet and evaluate every menu merchandise step-by-step to doc organic, chemical, and bodily dangers.
Itemizing too many CCPs
Over-marking steps as CCPs can overwhelm employees and distract focus from the really essential ones. Not each step is a CCP; some are managed by means of normal working procedures.
Sensible tip: Use a call tree to resolve if a step ought to be a CCP. Solely steps that immediately stop or remove a hazard ought to qualify.
Failing to calibrate thermometers commonly
Inaccurate thermometers give false confidence. Cooking to a “protected” temperature is meaningless if the instrument studying it’s off by 10 levels.
Sensible tip: Set a weekly schedule for thermometer calibration. Hold a log to confirm every gadget has been examined.
Poor recordkeeping
Incomplete, illegible, or backfilled logs put your operation in danger. Inspectors see poor information as indicators the plan isn’t actually adopted.
Sensible tip: Assign recordkeeping obligations by function and shift. Use checklists or digital instruments to standardize entries.
Not coaching all shifts
It is easy to coach the morning crew however neglect about night or part-time employees. This creates gaps in security and results in inconsistent practices.
Sensible tip: Schedule coaching throughout all shifts. Use brief, repeatable classes and require sign-offs from every workforce member.
Overcomplicating documentation
HACCP plans which are lengthy, technical, or crammed with authorized jargon will not be used day-to-day. Simplicity will increase usability.
Sensible tip: Use clear, plain language. Focus every part on what employees must know and do. Hold SOPs brief and visible the place attainable.
Protecting the plan clear, particular, and practical makes it simpler to your workforce to comply with it day by day.
What are the most effective HACCP ideas for various restaurant varieties?
The core HACCP steps are the identical for any meals service, however you may tailor the plan to your institution:
- Full-service and wonderful eating: Advanced menus and a number of cooking strategies imply many small CCPs. Pay shut consideration to processes like sous-vide, gradual cooking, sushi (uncooked fish), or any uncommon ingredient prep. Allergen controls are essential in wonderful eating; embody them in hazard evaluation. Workers coaching is essential – guarantee each prepare dinner understands the HACCP plan steps for every station (e.g., grill, oven, pastry).
- Fast-service (quick meals): Usually has a restricted menu and excessive quantity. Give attention to CCPs for gadgets like burgers or fried hen (temperatures, prepare dinner instances). Use standardized recipes and examine factors for meeting. Pre-made substances (sauce, salads) nonetheless want hazard checks (e.g., refrigeration, cross-contamination). Take into account emphasizing frequent grilling temp checks and rigorous cooling logs for giant batches.
- Catering and banquets: Off-site occasions pose distinctive dangers. Plan for prolonged transport, holding at occasions, and reheating on the venue. Cooling and reheating turn out to be CCPs: you need to chill meals sufficiently after prep and reheat them to the correct temperatures on website. Make sure that your plan covers closing dates for transport and holding (e.g., insulated containers, ice baths).
- Others (meals vans, cafeterias): Cell or large-scale kitchens ought to combine HACCP with native well being code. In meals vans, house is tight, so strict cross-contam controls (e.g., separate slicing boards, gloves) are a type of HACCP preventive management. Giant cafeterias usually use batch cooking – emphasize batch monitoring and staggered cooking/cooling schedules.
In each case, contain your workforce in writing the HACCP plan so it displays actual operations, and prepare employees on the way to comply with it. Energetic managerial management (supervisors checking logs and procedures) ought to reinforce the written plan.
Find out how to prepare your workforce to comply with the restaurant HACCP plan
A HACCP plan solely works in case your employees is aware of the way to carry it out. Coaching ought to be a part of the plan rollout and a recurring exercise in your meals security program.
Trainings ought to embody:
- Onboarding for brand spanking new staff: Each new rent ought to obtain HACCP coaching on their first day. This ensures they perceive your kitchen’s meals security priorities from the beginning, lowering the prospect of early errors.
- Palms-on demonstrations: Don’t depend on printed supplies alone. Present staff precisely the way to measure temperatures, fill out logs, and comply with CCP steps. Demonstrations assist reinforce muscle reminiscence and increase long-term adherence.
- Refresher coaching each 6-12 months or after main updates: Repetition ensures expertise keep sharp. Refresher classes also needs to be scheduled after any modifications to the menu, course of, or HACCP plan so everybody stays aligned.
- Signal-off sheets to substantiate coaching completion: Preserve proof of coaching as a part of your HACCP documentation. These information present auditors and inspectors that your employees has been correctly skilled and is accountable for meals security duties.
Coaching information are a part of your documentation. These assist confirm to inspectors that employees know the way to implement the plan appropriately.
Do you have to use digital HACCP logs or paper to watch meals security?
Whether or not you doc your HACCP plan on paper or in a digital system, the aim is identical: maintain clear, dependable information which are simple to replace and confirm.
Paper methods may match properly for small kitchens however will be more durable to audit, inclined to wreck, and require extra cupboard space.
Digital methods make it simpler to:
- Retailer and retrieve logs
- Set alerts for missed entries
- Robotically calculate temperature ranges
- Replace plan variations with out reprinting
Whichever you select, guarantee information are crammed out precisely, saved safely, and reviewed commonly. (After all, as a meals security administration software program firm, we’re biased, however we consider you should not delay digitizing meals security, and for this reason.)
Digitize your restaurant HACCP plan and meals security monitoring system
FoodDocs is the one digital answer that provides an AI-powered HACCP plan builder. In only one hour, you may get a complete and dealing HACCP plan — based mostly in your particular enterprise operations — that you would be able to begin utilizing shortly in your HACCP system. No extra lengthy hours of conferences and revisions.
And, if wanted, you may totally customise the HACCP plan and make updates as your operations change or based mostly on an inspector’s or auditor’s suggestions!


FoodDocs’ HACCP system additionally helps your monitoring and traceability wants
The good HACCP system contains an important parts of a meals security plan by getting your solutions to fundamental questions in the course of the setup course of.
Our answer cross-references the knowledge with our digital meals security data library and makes use of synthetic intelligence to generate the template. Among the meals security questions embody:
- What’s what you are promoting kind?
- What uncooked supplies are used?
- What sort of meals do you promote?
- How massive is the quantity?
- What duties do you’ve gotten in what you are promoting?

As seen within the instance of the HACCP plan above, our digital answer can generate an important info for you. What’s even higher is that you would be able to customise the knowledge to suit your enterprise higher.
Our system generates a customizable HACCP plan template based mostly in your solutions to some questions on what you are promoting. This helps us determine the required procedures and varieties associated to your meals enterprise and tailor the HACCP plan for you.
Right here is an instance of the contents of a HACCP plan template you’ll get while you enroll with us at FoodDocs.
- Primary and superior prerequisite applications
- Circulation chart of your meals operations
- Identification of hazards and an entire evaluation desk
- Established essential management factors
- Established essential limits
- CCP monitoring procedures
- Verification procedures
- File-keeping and documentation procedures
Along with the AI-powered HACCP Plan builder, FoodDocs additionally provides an all-in-one meals security monitoring and traceability system. Take a look at the two-minute FSMS explainer video beneath:

Ceaselessly requested questions on restaurant HACCP plans
















